Abstract
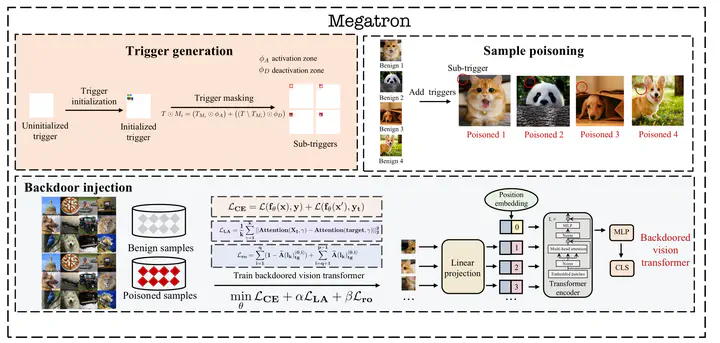
Vision transformers have achieved impressive performance in various vision-related tasks, but their vulnerability to backdoor attacks is under-explored. A handful of existing works mainly adapt CNN-oriented backdoor attacks to vision transformers with visible triggers susceptible to state-of-the-art backdoor defenses. In this paper, we propose MEGATRON, a stealthy backdoor attack framework especially targeting vision transformers. The backdoor trigger is processed with masking operations to preserve its effectiveness and concealment as input images are converted into one-dimensional tokens by the transformer model. We discover that training the transformer model with standard backdoor loss functions yields poor attack performance. To address this difficulty, we design two loss terms to improve the attack performance. We propose latent loss to minimize the distance between the backdoored sample and the clean sample of the target label for each layer’s attention. We propose attention diffusion loss to emphasize the importance of the attention diffusion area while reducing the importance of the non-diffusion area during training. We also provide a theoretical analysis that elucidates the rationale behind the attention diffusion loss. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, GTSRB, CIFAR-100, and Tiny ImageNet demonstrate that MEGATRON outperforms state-of-the-art vision transformer backdoor attacks. With a trigger as small as 4 pixels, MEGATRON is able to realize a 100% attack success rate. Furthermore, MEGATRON achieves better evasiveness than baselines in terms of both human visual inspection and defense strategies. We will open-source our codes upon publication.